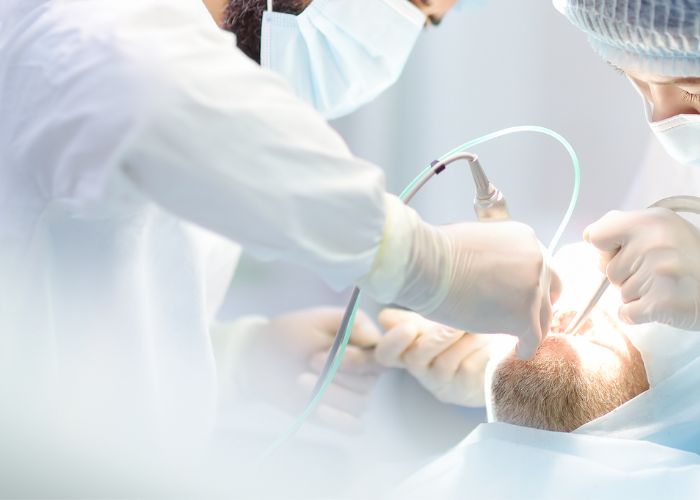
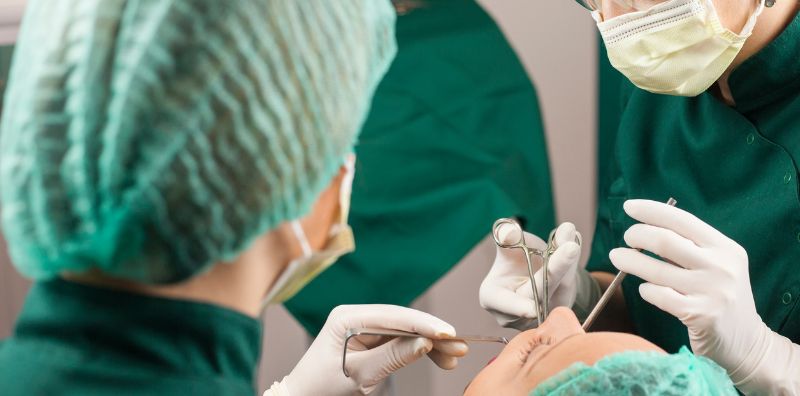
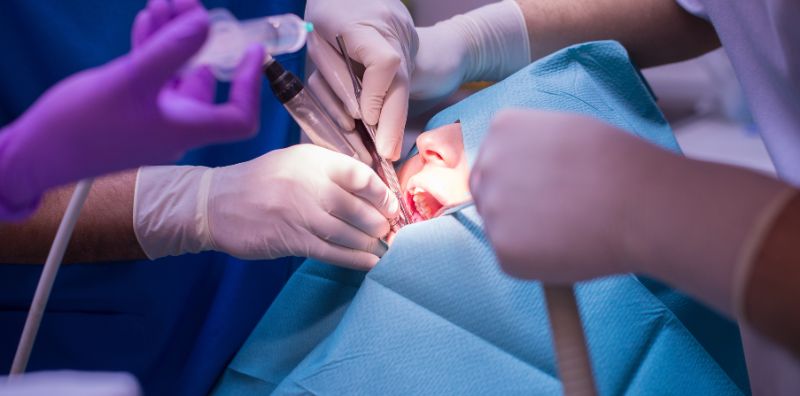
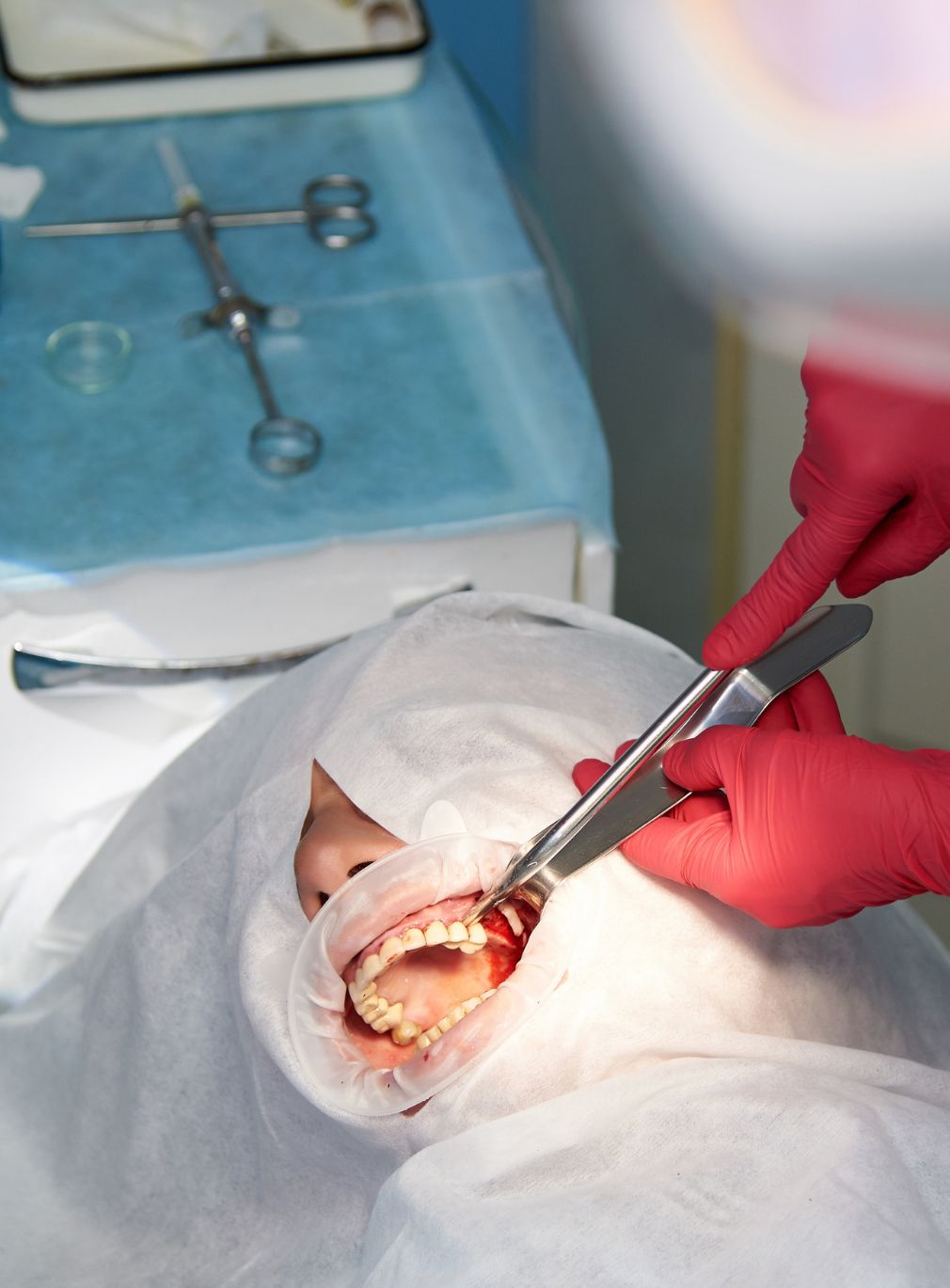
Oral Surgery
Optimize your gum health and address oral issues with our specialization in periodontics. Benefit from advanced solutions through our expertise in oral surgery, ensuring a healthy and balanced smile.
- Dental Extractions
- Wisdom Teeth Surgery
- Gum Surgery
- Oral Biopsies
- Periodontics
Oral Surgery
What is oral surgery and when is it recommended?
Oral surgery encompasses a set of surgical procedures performed within the oral cavity and surrounding structures. It is recommended to treat a variety of conditions such as complex extractions, gum and mucosal diseases, as well as oral lesions.
What types of dental extractions are performed in oral surgery?
In oral surgery, various types of dental extractions can be performed, including wisdom tooth extractions, impacted tooth extractions, extractions of damaged or infected teeth, as well as other complex extractions requiring surgical intervention.
How is wisdom tooth surgery performed?
Wisdom tooth surgery typically involves local or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the procedure. The oral surgeon makes an incision in the gum to access the wisdom tooth, then removes the tooth in pieces if necessary. After the extraction, stitches may be placed to close the wound.
What is periodontitis and what are its symptoms?
Periodontitis is a disease affecting the supporting tissues of the teeth, particularly the gums and the bone surrounding the tooth root. It begins with gum inflammation, called gingivitis, caused by plaque buildup around the neck of the tooth. Common symptoms of periodontitis include:
- Red and swollen gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Gum recession (gums pulling away from the teeth)
- Persistent bad breath
- Periodontal pockets
- Tooth mobility
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a dentist promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
How can periodontitis be prevented?
The prevention of periodontitis mainly relies on good oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist. Here are some tips to prevent this disease:
- Tooth brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to brush all surfaces of the teeth and gently massage the gums.
- Flossing: Use dental floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between the teeth and below the gum line, where the toothbrush cannot reach.
- Balanced diet: Adopt a healthy, balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, and limit the intake of sugar and processed foods.
- Regular dental visits: See your dentist for regular examinations and professional cleanings, usually every six months. These visits help detect early signs of gingivitis or periodontitis and allow for prompt intervention.
- Avoid tobacco: Tobacco is a major risk factor for periodontitis. Quitting smoking or avoiding tobacco products can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum diseases.
- Manage stress: Stress can weaken your immune system and make it harder to fight infections, including periodontal diseases. Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation, exercise, or other relaxing activities.
By following these tips, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing periodontitis and maintain good oral health.
What is orthognathic surgery and what problems can it correct?
Orthognathic surgery is a surgical procedure used to correct jaw and teeth alignment anomalies. It may be recommended to address issues such as crossbites, prognathism, retrognathism, and other severe malocclusions that cannot be corrected by orthodontic treatments alone.
Wisdom teeth extraction
Wisdom teeth extraction is a common surgical procedure performed to remove the third molars, commonly referred to as wisdom teeth. This intervention may be necessary when these teeth cannot emerge properly in the dental arch, leading to potential complications. Let’s explore the details of this procedure.
Evaluation and Planning
Before the extraction of wisdom teeth, a thorough evaluation is conducted by the oral surgeon to determine the position of the wisdom teeth, their state of development, and whether there are potential complications such as impaction. Based on this evaluation, a treatment plan is established to determine the best timing and appropriate surgical approach.
Extraction Procedure
The wisdom teeth extraction procedure is typically performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the complexity of the situation and the patient’s preferences. The oral surgeon makes an incision in the gum to access the wisdom tooth, then removes it in pieces if necessary. After the extraction, stitches may be placed to close the wound.
Post-Operative Care
After the extraction of wisdom teeth, post-operative instructions are provided to the patient to promote quick healing and minimize complications. This may include applying cold compresses to reduce swelling, using pain relievers to manage discomfort, sticking to a soft diet for a few days, and observing good oral hygiene practices to avoid infections.